고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문

Dioxus 예제 저장소는 10개의 개별 카테고리로 구성된 포괄적인 학습 리소스로, 각 카테고리는 프레임워크 기능의 구체적인 측면을 보여주도록 설계되었습니다. 이러한 예제는 교육 자료이자 실제 애플리케이션 구축을 위한 실질적인 시작점 역할을 합니다.
예시 조직
이러한 예제는 개발자가 기본 개념에서 고급 패턴까지 이해할 수 있도록 계층적으로 구성되어 있습니다.
| 범주 | 집중 | 주요 주제 |
| 01-app-demos | 신청서 작성 | 실제 앱, UI 패턴 |
| 02-building-ui | UI 구성 요소 | 대화형 요소, SVG |
| 03-assets-styling | 자산 및 CSS | 동적 자산, 메타 태그 |
| 04-managing-state | 국가 관리 | 신호, 컨텍스트, 리듀서 |
| 05-using-async | 비동기 작업 | 선물, 스트림, 서스펜스 |
| 06-routing | 항해 | 라우터, 쿼리 매개변수 |
| 07-fullstack | 서버 통합 | 서버 기능, SSR |
| 08-apis | 플랫폼 API | 파일 처리, 윈도우 |
| 09-reference | 언어 특징 | RSX 패턴, 제네릭 |
| 10-integrations | 외부 도구 | 테일윈드, 베비, PWA |
실행 예제
기본 예제
간단한 예제는 Cargo를 사용하여 직접 실행할 수 있습니다.
cargo run --example hello_world
# Run with specific platform features
cargo run --example calculator --features desktop
예를 들어, hello_world.rs 는 기본 구조를 보여줍니다.
use dioxus::prelude::*;
fn main() {
dioxus::launch(app);
}
fn app() -> Element {
rsx! {
div { "Hello, world!" }
}
}
복잡한 예
더욱 정교한 예에는 고유한 Cargo.toml구성이 포함되며 특정 기능이 필요할 수 있습니다.
# Navigate to example directory
cd examples/01-app-demos/calculator
# Run with platform-specific features
cargo run --features desktop
계산기 예제는 키보드 이벤트 처리와 사용자 정의 스타일을 사용한 고급 상태 관리를 보여줍니다.
use dioxus::events::*;
use dioxus::html::input_data::keyboard_types::Key;
use dioxus::prelude::*;
const STYLE: Asset = asset!("assets/calculator.css");
fn main() {
dioxus::LaunchBuilder::desktop()
.with_cfg(desktop!({
use dioxus::desktop::{Config, LogicalSize, WindowBuilder};
Config::new().with_window(
WindowBuilder::default()
.with_title("Calculator")
.with_inner_size(LogicalSize::new(300.0, 525.0)),
)
}))
.launch(app);
}
fn app() -> Element {
let mut val = use_signal(|| String::from("0"));
let mut input_digit = move |num: String| {
if val() == "0" {
val.set(String::new());
}
val.push_str(num.as_str());
};
let mut input_operator = move |key: &str| val.push_str(key);
let handle_key_down_event = move |evt: KeyboardEvent| match evt.key() {
Key::Backspace => {
if !val().is_empty() {
val.pop();
}
}
Key::Character(character) => match character.as_str() {
"+" | "-" | "/" | "*" => input_operator(&character),
"0" | "1" | "2" | "3" | "4" | "5" | "6" | "7" | "8" | "9" => input_digit(character),
_ => {}
},
_ => {}
};
rsx! {
Stylesheet { href: STYLE }
div { id: "wrapper",
div { class: "app",
div { class: "calculator", tabindex: "0", onkeydown: handle_key_down_event,
div { class: "calculator-display",
if val().is_empty() {
"0"
} else {
"{val}"
}
}
div { class: "calculator-keypad",
div { class: "input-keys",
div { class: "function-keys",
button {
class: "calculator-key key-clear",
onclick: move |_| {
val.set(String::new());
if !val.cloned().is_empty() {
val.set("0".into());
}
},
if val.cloned().is_empty() { "C" } else { "AC" }
}
button {
class: "calculator-key key-sign",
onclick: move |_| {
let new_val = calc_val(val.cloned().as_str());
if new_val > 0.0 {
val.set(format!("-{new_val}"));
} else {
val.set(format!("{}", new_val.abs()));
}
},
"±"
}
button {
class: "calculator-key key-percent",
onclick: move |_| val.set(format!("{}", calc_val(val.cloned().as_str()) / 100.0)),
"%"
}
}
div { class: "digit-keys",
button {
class: "calculator-key key-0",
onclick: move |_| input_digit(0.to_string()),
"0"
}
button {
class: "calculator-key key-dot",
onclick: move |_| val.push('.'),
"●"
}
for k in 1..10 {
button {
class: "calculator-key {k}",
name: "key-{k}",
onclick: move |_| input_digit(k.to_string()),
"{k}"
}
}
}
}
div { class: "operator-keys",
for (key, class) in [("/", "key-divide"), ("*", "key-multiply"), ("-", "key-subtract"), ("+", "key-add")] {
button {
class: "calculator-key {class}",
onclick: move |_| input_operator(key),
"{key}"
}
}
button {
class: "calculator-key key-equals",
onclick: move |_| val.set(format!("{}", calc_val(val.cloned().as_str()))),
"="
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
fn calc_val(val: &str) -> f64 {
let mut temp = String::new();
let mut operation = "+".to_string();
let mut start_index = 0;
let mut temp_value;
let mut fin_index = 0;
if &val[0..1] == "-" {
temp_value = String::from("-");
fin_index = 1;
start_index += 1;
} else {
temp_value = String::from("");
}
for c in val[fin_index..].chars() {
if c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*' || c == '/' {
break;
}
temp_value.push(c);
start_index += 1;
}
let mut result = temp_value.parse::<f64>().unwrap();
if start_index + 1 >= val.len() {
return result;
}
for c in val[start_index..].chars() {
if c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*' || c == '/' {
if !temp.is_empty() {
match &operation as &str {
"+" => result += temp.parse::<f64>().unwrap(),
"-" => result -= temp.parse::<f64>().unwrap(),
"*" => result *= temp.parse::<f64>().unwrap(),
"/" => result /= temp.parse::<f64>().unwrap(),
_ => unreachable!(),
};
}
operation = c.to_string();
temp = String::new();
} else {
temp.push(c);
}
}
if !temp.is_empty() {
match &operation as &str {
"+" => result += temp.parse::<f64>().unwrap(),
"-" => result -= temp.parse::<f64>().unwrap(),
"*" => result *= temp.parse::<f64>().unwrap(),
"/" => result /= temp.parse::<f64>().unwrap(),
_ => unreachable!(),
};
}
result
}
플랫폼별 구성
데스크톱 애플리케이션
데스크톱 예제는 LaunchBuilder플랫폼별 구성에 사용됩니다.
dioxus::LaunchBuilder::desktop()
.with_cfg(desktop!({
use dioxus::desktop::{Config, LogicalSize, WindowBuilder};
Config::new().with_window(
WindowBuilder::default()
.with_title("Calculator")
.with_inner_size(LogicalSize::new(300.0, 525.0)),
)
}))
.launch(app);웹 애플리케이션
web해당 기능이 활성화되면 웹 예제는 브라우저 배포를 위해 자동으로 구성됩니다 .
[features]
default = ["web"]
web = ["dioxus/web"]통합 예제
Tailwind CSS 와 같은 외부 통합의 예로는 자산 관리가 있습니다.
rsx! {
Stylesheet { href: asset!("/assets/tailwind.css") }
div {
class: "container mx-auto flex flex-wrap p-5",
// Tailwind classes...
}
}
개발 워크플로
핫 리로딩
많은 예제에서 개발 중 핫 리로딩을 지원합니다. 다음을 통해 활성화할 수 있습니다.
dx serve --example your_example_name자산 관리
asset!정적 자산에 대한 매크로를 사용하는 예 :
const STYLE: Asset = asset!("/examples/assets/calculator.css");
assets 디렉토리 에는 여러 예제에서 사용되는 공유 CSS 파일이 들어 있습니다.
구성 파일
복잡한 예로는 Dioxus.toml애플리케이션 메타데이터가 있습니다.
[application]
name = "hot_dog"
[bundle]
identifier = "com.dioxuslabs"
publisher = "Dioxus Labs"
학습 경로
초보자의 경우 다음 예시를 따라 진행해 보세요.
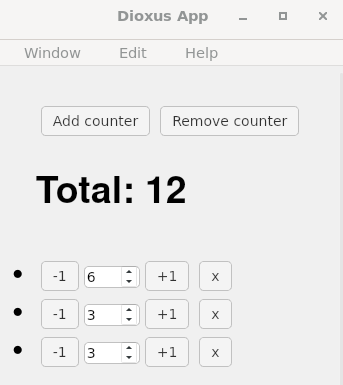
examples/01.app-demo/counters.rs
//! A simple counters example that stores a list of items in a vec and then iterates over them.
use dioxus::prelude::*;
const STYLE: Asset = asset!("/examples/assets/counter.css");
fn main() {
dioxus::launch(app);
}
fn app() -> Element {
// Store the counters in a signal
let mut counters = use_signal(|| vec![0, 0, 0]);
// Whenever the counters change, sum them up
let sum = use_memo(move || counters.read().iter().copied().sum::<i32>());
rsx! {
Stylesheet { href: STYLE }
div { id: "controls",
button { onclick: move |_| counters.push(0), "Add counter" }
button { onclick: move |_| { counters.pop(); }, "Remove counter" }
}
h3 { "Total: {sum}" }
// Calling `iter` on a Signal<Vec<>> gives you a GenerationalRef to each entry in the vec
// We enumerate to get the idx of each counter, which we use later to modify the vec
for (i, counter) in counters.iter().enumerate() {
// We need a key to uniquely identify each counter. You really shouldn't be using the index, so we're using
// the counter value itself.
//
// If we used the index, and a counter is removed, dioxus would need to re-write the contents of all following
// counters instead of simply removing the one that was removed
//
// You should use a stable identifier for the key, like a unique id or the value of the counter itself
li { key: "{i}",
button { onclick: move |_| counters.write()[i] -= 1, "-1" }
input {
r#type: "number",
value: "{counter}",
oninput: move |e| {
if let Ok(value) = e.parsed() {
counters.write()[i] = value;
}
}
}
button { onclick: move |_| counters.write()[i] += 1, "+1" }
button { onclick: move |_| { counters.remove(i); }, "x" }
}
}
}
}
예제 실행 및 결과
cargo run --example hello_world --features desktop
cargo run --example calculator --features desktop

cargo run --example counters --features desktop
예제 소스를 파악하시고 실행을 해보시길 바랍니다. 다음에도 예제에 대한 소스 코드와 실행을 해보는 시간을 가져볼게요.




